Скачать с ютуб Equilibrium Graphs: Le Chatelier's Principle (Chemical Equilibrium). в хорошем качестве
le chatelier's principle graphs
le chatelier's principle equilibrium graph
chemical equilibrium graph
chemical equilibrium graph explanation
equilibrium graph
equilibrium graph chemistry
chemical equilibrium graph problems
le chatelier's principle
chemical equilibrium graphs
graphing
chemical equilibrium
equilibrium
equilibrium graphs examples
graph
add
remove
reactant
product
temperature change
pressure change
chemistry
grade 12
problems
education
instructor johnny
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Equilibrium Graphs: Le Chatelier's Principle (Chemical Equilibrium). в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Equilibrium Graphs: Le Chatelier's Principle (Chemical Equilibrium). или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Equilibrium Graphs: Le Chatelier's Principle (Chemical Equilibrium). в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Equilibrium Graphs: Le Chatelier's Principle (Chemical Equilibrium).
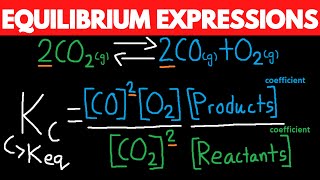
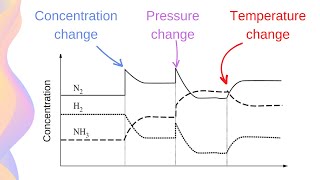
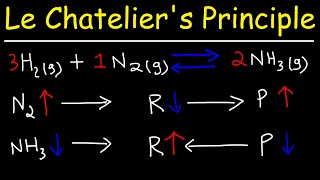
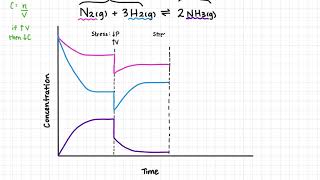
This Chemistry video explains Le Chatelier's Principle equilibrium graphs and how to graph equilibrium shifts In this video you will learn how to graph equilibrium shifts or changes and interpret equilibrium graphs. It also shows you how to identify when the equilibrium occurs on a concentration vs time graph and a forward reaction vs reverse reaction graph. This video contains an abundance of practice problems and examples to work through. What are you waiting for? It's time to learn! :D ()()():)()()() 🍎 𝐑𝐞𝐝𝐨𝐱 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐄𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐡𝐞𝐦𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐲 𝐓𝐮𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐚𝐥𝐬: https://bit.ly/RedoxElectrochemistry ⚗️ 𝐂𝐡𝐞𝐦𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐄𝐪𝐮𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐛𝐫𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐀𝐜𝐢𝐝-𝐁𝐚𝐬𝐞 𝐒𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦𝐬 𝐓𝐮𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐚𝐥𝐬: https://bit.ly/EquilibriumAcidsBases 🧪 𝐂𝐡𝐞𝐦𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐲 𝟑𝟎 (𝐆𝐫𝐚𝐝𝐞 𝟏𝟐) 𝐓𝐮𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐚𝐥𝐬: https://bit.ly/Johnny_Chemistry30 Follow me for updates and behind the scenes: 📸 Instagram: https://bit.ly/3mPb2q7 ()()():)()()() Graphing equilibrium shifts for a chemical reaction and interpreting equilibrium graphs is a concept present in the Chemical Equilibrium unit in Chemistry 30 (grade 12 level). When a system reaches equilibrium, the concentrations of all the substances will remains constant (not changing amount). On a graph, that situation can be visualized as a straight line; therefore, equilibrium is reached when the reactants and products have straight lines. Dynamic equilibrium is reached when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. On a graph, dynamic equilibrium is reached when the lines are equal (on top of each other). Concentration changes on a graph: When a substance is added or removed, it changes concentration and in turn causes the reaction to shift. The reaction will shift to use up what is added or shift to replace what is loss. On a graph, one substance will immediately increase or decrease (depending on the stress) Then all the substances will increase or decrease depending on the effect of the equilibrium shift. Temperature changes on a graph: -The effect of increasing temperature or decreasing temperature on an equilibrium reaction depends on whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic. The reaction will shift to use up excess energy (heat/temperature) or shift to replace loss energy (heat/temperature). On a graph, all substances will increase or decrease only depending on the effect of the equilibrium shift. Only temperature changes can change the Kc value; therefore, on a graph the Kc value should either decrease or increase in value. Pressure changes on graph: When pressure increases or volume decreases, the reaction will shift to the side with less gas mols to relieve the system of the extra pressure. When pressure decreases or volume increases, the reaction will shift to the side with greater gas mols to replace the loss pressure. On a graph, all substances will immediately increase or decrease. If pressure increases, everything will increase. If pressure decrease everything will decrease. Then all the substances will increase or decrease depending on the effect of the equilibrium shift. ()()():)()()() Concentration vs Time Graph - 0:00 Forward Reaction vs Reverse Reaction Graph - 0:37 Equilibrium Shift on a Graph (adding) - 0:57 Equilibrium Shift on a Graph (removing) - 1:49 Equilibrium Shift on a Graph (temperature) - 2:27 Equilibrium Shift on a Graph (pressure) - 3:02 Practice Problem - 3:58 Remember Notes - 6:03 Bye-Bye - 6:56