Скачать с ютуб Meiosis in bengali/ different stages of meiosis/Class 10 life science/ Meiotic Cell division/wbcs в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Meiosis in bengali/ different stages of meiosis/Class 10 life science/ Meiotic Cell division/wbcs в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Meiosis in bengali/ different stages of meiosis/Class 10 life science/ Meiotic Cell division/wbcs или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Meiosis in bengali/ different stages of meiosis/Class 10 life science/ Meiotic Cell division/wbcs в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Meiosis in bengali/ different stages of meiosis/Class 10 life science/ Meiotic Cell division/wbcs
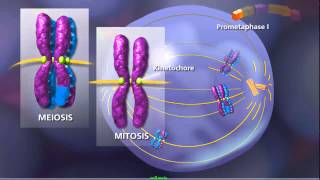
Meiosis in bengali/ different stages of meiosis/Class 10 life science/ Meiotic Cell division/wbcs Here the basic principles of Meiosis are described in context of the syllabus of WBBSE for the students of class 10.মিয়োসিস কোষ বিভাজন কাকে বলে, মিয়োসিসের কয়টি পর্যায়, মিয়োসিস কোষ বিভাজনের গুরুত্ব, চিহ্নিত চিত্র সহকারে ক্রসিং ওভার এর বর্ণনা করা হয়েছে. Meiosis, on the other hand, is used for just one purpose in the human body: the production of gametes—sex cells, or sperm and eggs. Its goal is to make daughter cells with exactly half as many chromosomes as the starting cell. To put that another way, meiosis in humans is a division process that takes us from a diploid cell—one with two sets of chromosomes—to haploid cells—ones with a single set of chromosomes. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a complete diploid set: a new genome. meiosis using a two-step division process. Homologous pairs separate during a first round of cell division, called meiosis I. Sister chromatids separate during a second round, called meiosis II.Meiosis 1 Stages The different stages of meiosis 1 can be explained by the following phases : Phases of Meiosis 1 Prophase 1 Metaphase 1 Anaphase 1 Telophase Phases of prophase 1 Prophase I is longer than the mitotic prophase and is further subdivided into 5 substages, leptotene zygotene pachytene diplotene diakinesis The chromosomes begin to condense and attain a compact structure during leptotene. In zygotene, the pairing of homologous chromosomes starts a process known as chromosomal synapsis, accompanied by the formation of a complex structure called synaptonemal complex. A pair of synapsed homologous chromosome forms a complex known as bivalent or tetrad. At pachytene stage, crossing over of non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes occurs at the recombination nodules. The chromosomes remain linked at the sites of crossing over. Diplotene marks the dissolution of the synaptonemal complex and separation of the homologous chromosomes of the bivalents except at the sites of cross-over. The X-shaped structures formed during separation are known as chiasmata. Diakinesis is marked by the termination of chiasmata and assembly of the meiotic spindle to separate the homologous chromosomes. The nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Meiosis II is almost like mitosis.







![SSC Biology Chapter 3 | Cell Division [ কোষ বিভাজন ] || Fahad Sir](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/4dGAIL8FYZk/mqdefault.jpg)