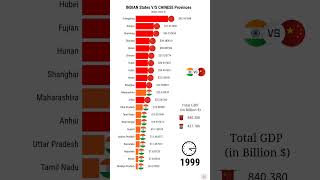
Скачать с ютуб India beat Africa | GDP Comparison Indian States VS African Countries (1970-2022) в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок India beat Africa | GDP Comparison Indian States VS African Countries (1970-2022) в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно India beat Africa | GDP Comparison Indian States VS African Countries (1970-2022) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон India beat Africa | GDP Comparison Indian States VS African Countries (1970-2022) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
India beat Africa | GDP Comparison Indian States VS African Countries (1970-2022)
The economy of India is characterised as a middle income developing market economy. It is the world's sixth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), on a per capita income basis, India ranked 145th by GDP (nominal) and 122th by GDP (PPP). From independence in 1947 until 1991, successive governments promoted protectionist economic policies, with extensive state intervention and economic regulation. This is characterised as dirigism, in the form of the License Raj.The end of the Cold War and an acute balance of payments crisis in 1991 led to the adoption of a broad economic liberalisation in India. Since the start of the 21st century, annual average GDP growth has been 6% to 7%, and from 2013 to 2018, India was the world's fastest growing major economy, surpassing China. Historically, India was the largest economy in the world for most of the two millennia from the 1st until the 19th century. The long-term growth perspective of the Indian economy remains positive due to its young population and corresponding low dependency ratio, healthy savings, and investment rates, increasing globalisation in India and integration into the global economy. The economy slowed in 2017, due to shocks of "demonetisation" in 2016 and the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax in 2017. Nearly 60% of India's GDP is driven by domestic private consumption. The country remains the world's sixth-largest consumer market. Apart from private consumption, India's GDP is also fueled by government spending, investment, and exports. In 2019, India was the world's ninth-largest importer and the twelfth-largest exporter. India has been a member of the World Trade Organization since 1 January 1995. It ranks 63rd on the Ease of doing business index and 68th on the Global Competitiveness Report. With 500 million workers, the Indian labour force was the world's second-largest as of 2019. India has one of the world's highest number of billionaires and extreme income inequality.Since India has a vast informal economy, barely 2% of Indians pay income taxes Sources: ...... The economy of Africa consists of the trade, industry, agriculture, and human resources of the continent. As of 2019, approximately 1.3 billion peoplewere living in 54 countries in Africa. Africa is a resource-rich continent.Recent growth has been due to growth in sales in commodities, services, and manufacturing.West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa and Southern Africa in particular, are expected to reach a combined GDP of $29 trillion by 2050. In March 2013, Africa was identified as the world's poorest inhabited continent; however, the World Bank expects that most African countries will reach "middle income" status (defined as at least US$1,025 per person a year) by 2025 if current growth rates continue.[16] There are a number of reasons for Africa's poor economy: historically, even though Africa had a number of empires trading with many parts of the world, many people lived in rural societies; in addition, European colonization and the later Cold War created political, economic and social instability.[17] However, as of 2013 Africa was the world's fastest-growing continent at 5.6% a year, and GDP is expected to rise by an average of over 6% a year between 2013 and 2023. In 2017, the African Development Bank reported Africa to be the world's second-fastest growing economy, and estimates that average growth will rebound to 3.4% in 2017, while growth is expected to increase by 4.3% in 2018.Growth has been present throughout the continent, with over one-third of African countries posting 6% or higher growth rates, and another 40% growing between 4% to 6% per year. Following the independence of African countries during the 20th century, economic, political and social upheaval consumed much of the continent. An economic rebound among some countries has been evident in recent years, however. The dawn of the African economic boom (which is in place since the 2000s) has been compared to the Chinese economic boom that had emerged in Asia since late 1970s.in 2013, Africa was home to seven of the world's fastest-growing economies. As of 2018, Nigeria is the biggest economy in Africa by nominal GDP, followed by South Africa; in terms of PPP, Egypt is second biggest after Nigeria. Sources: https://m.statisticstimes.com/economy... http://www.macrotrends.net/ http://censusindia.gov.in/ music credit: / @alexproductionsnocopyright