Скачать с ютуб Mitochondria & Plastids |Class 11|chapter 3|Biology в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Mitochondria & Plastids |Class 11|chapter 3|Biology в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Mitochondria & Plastids |Class 11|chapter 3|Biology или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Mitochondria & Plastids |Class 11|chapter 3|Biology в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Mitochondria & Plastids |Class 11|chapter 3|Biology
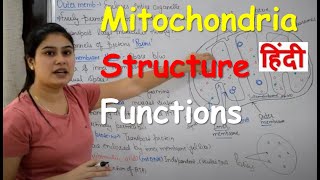
Mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell" because they produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy currency of cells. They have a double membrane structure, with an inner membrane that is highly folded into structures called cristae, which increases the surface area for energy production. Mitochondria also play roles in regulating metabolism, apoptosis (programmed cell death), and calcium homeostasis. Interestingly, they have their own DNA, which is inherited maternally, supporting the theory of their evolutionary origin from ancestral prokaryotic cell. Structure of Mitochondria 1. **Outer Membrane**: Smooth and permeable to small molecules and ions. 2. **Inner Membrane**: Highly folded into cristae, which increase surface area and house the proteins involved in electron transport and ATP synthesis. 3. **Intermembrane Space**: The space between the outer and inner membranes, involved in the process of energy production. 4. **Matrix**: The innermost compartment, containing enzymes for the citric acid cycle, mitochondrial DNA, and ribosomes. Functions of Mitochondria 1. **ATP Production**: Through oxidative phosphorylation, mitochondria convert nutrients into ATP, the cell’s energy currency. 2. **Metabolism**: Involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. 3. **Apoptosis**: Play a key role in programmed cell death, releasing factors that activate cell death pathways. 4. **Calcium Homeostasis**: Help regulate calcium levels in cells, crucial for various cellular processes. 5. **Heat Production**: In brown adipose tissue, mitochondria generate heat through non-shivering thermogenesis. These functions are essential for maintaining cellular health and energy balance.
![Будова клітини [Nucleus Medical Media]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/bBymW0PtVT0/mqdefault.jpg)