Скачать с ютуб Anterior triangle of the neck в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Anterior triangle of the neck в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Anterior triangle of the neck или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Anterior triangle of the neck в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
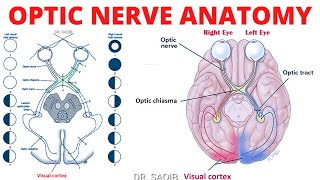
Anterior triangle of the neck
Anterior triangle of the neck: Dr. Saqib The video contains a detailed account of anterior triangle of neck. Its boundaries, subdivisions,into four triangles, contents of each of these four subdivisions. Boundaries of anterior triangle: • Anterior boundary: median line of the neck. • Posterior boundary: anterior border of the SCM. • Superior boundary: inferior border of the mandible. • Apex: at the jugular notch in the manubrium. • Roof: formed by subcutaneous tissue which contains the platysma. • Floor: Constituted by the pharynx, larynx, and thyroid gland. Subdivisions of Anterior Triangle: The region is subdivided into four smaller triangles. This division is sub served by the digastric and omohyoid muscles: 1 Unpaired: submental triangle 3 small paired triangles: submandibular carotid, and muscular. 1. Submental triangle: Placed inferior to the chin, in the suprahyoid area. Boundaries: Inferiorly: body of the hyoid Laterally: right and left anterior bellies of digastric muscles. Floor: two mylohyoid muscles, (median fibrous raphe). Base: formed by the hyoid. Apex: lies at the mandibular symphysis. Contents of Submental triangle: Numerous little submental lymph nodes and small veins that form the anterior jugular vein. 2. Submandibular or digastric triangle: Boundaries: Inferior border of mandible Anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric muscle. Floor: constituted by mylohyoid and hyoglossus muscles, and the middle pharyngeal constrictor. Contents of Submandibular or Digastric triangle: Anteriorly: Structures superficial to mylohyoid: Superficial portion of submandibular gland. Facial V. and submandibular lymph nodes are superficial to it and facial art deep. Submental artery Mylohyoid nerve and vessels Structures superficial to hyoglossus: Submandibular gland Intermediate tendon of digastric and stylohyoid Hypoglossal nerve Posteriorly: Superficially following are lying: Lower part of parotid gland External carotid artery before entrance to parotid gland Deeply placed structures: 1. Styloglossus 2. Stylopharyngeus 3. Glossopharyngeal nerve 4. Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve 5. A part of parotid gland 6. Styloid process Deepest structures: 1. Internal carotid artery 2. Vagus Nerve 3. Internal jugular vein 3. Carotid triangle: Boundaries: superior belly of the omohyoid, the posterior belly of the digastric, and the anterior border of the Sternocleidomastoid. Importance: It is so as the common carotid artery rises into it. Its pulse can be taken here. Contnents: ARTERIES: 1. Common carotid artery, with carotid body and carotid sinus 2. Internal carotid artery 3. External carotid artery with its facial, lingual, superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal and occipital branches. VEINS: 1. Internal jugular vein 2. Common facial vein 3. Lingual vein NERVES: 1. Hypoglossal nerve 2. Vagus nerve 3. Spinal accessory nerve 4. Superior laryngeal branch of vagus with its external and internal laryngeal branches Carotid Sinus: Dilation at the beginning of the internal carotid artery, which can involve the common carotid artery also. Carotid Body: Closely related to carotid sinus. It is a tiny, reddish brown rounded tissue that lies in a septum on the medial side of the common carotid artery where it divides. Innervation: Mainly, the glossopharyngeal nerve via the carotid sinus nerve, and the vagus nerve too. It is a baroreceptor (pressoreceptor) that responds when arterial blood pressure is altered. 4. Muscular Triangle: Boundaries: Superior belly of the omohyoid muscle, the anterior border of the SCM, and the median plane of the neck. Contents: infrahyoid muscles viscera (the thyroid and parathyroid glands for instance).






![Биология поведения человека. Лекция #1. Введение [Роберт Сапольски, 2010. Стэнфорд]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ik9t96SMtB0/mqdefault.jpg)