Скачать с ютуб Topic (02) Classification of Antibiotics | Different Method of Classification of Antibiotics в хорошем качестве
mechanism of action of antibiotics
mechanism of Action of antibiotics
mechanism of action of Antibiotics
classification of antibiotics
Classification of antibiotics
classification of antibiotics based on mechanism of
classification of Antibiotics as per mechanism of action
antibiotics MOA
classes of antibiotics
Antibiotics classification based on mechanism of action
Antibiotics Classification
Classification of Antibiotic
Antibiotics mechanism of action
ANTIBIOTICS
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Topic (02) Classification of Antibiotics | Different Method of Classification of Antibiotics в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Topic (02) Classification of Antibiotics | Different Method of Classification of Antibiotics или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Topic (02) Classification of Antibiotics | Different Method of Classification of Antibiotics в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Topic (02) Classification of Antibiotics | Different Method of Classification of Antibiotics
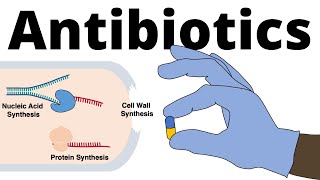
Download the "Solution Pharmacy" Mobile App to Get All Uploaded Notes, Model Question Papers, Answer Papers, Online Tests and other GPAT Materials - https://play.google.com/store/apps/de... Medicinal Chemistry Unit 01 Syllabus - (A) Antibiotics - Historical background, nomenclature, stereochemistry, structure-activity relationship, chemical degradation, classification and important product of these classes - (01) Beta-lactam antibiotics - Penicillin, Cephalosporins, beta-lactamase inhibitors, Monobactam (02) Aminoglycosides - Streptomycin, Neomycin, Kanamycin (03) Tetracycline - tetracycline, Oxytetracycline, Chlortetracycline, Minocycline, Doxycycline Introduction to Antibiotics Antibiotics are chemical compounds used to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. Strictly speaking, antibiotics are a subgroup of organic anti-infective agents that are derived from bacteria or moulds that are toxic to other bacteria. The term antibiotic may be used interchangeably with the term antibacterial. History of antibiotics Penicillin was the first antibiotic used successfully in treating bacterial infections. Sir Alexander Fleming first discovered it in 1928, but its potential for treatment against infections wasn’t recognised until over a decade later when Ernst B Chain, Sir Howard Florey and Norman Heatley produced enough purified penicillin to treat patients with. By the 1950s, a large number of antibiotics were being discovered and manufactured for the treatment of diseases caused by infecting bacteria. Over the last 50 years, antibiotics have transformed the patterns of disease and death. Classification of antibiotics Antibiotics can be classified in several ways. The most common method classifies them according to their chemical structure as antibiotics sharing the same or similar chemical structure will generally show similar patterns of antibacterial activity, effectiveness, toxicity and allergic potential. 1. B-lactam antibiotics inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. They include: Penicillins, Penicillin G, Amoxicillin, Flucloxacillin CephalosporinsCefoxitin, Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, Carbapenem 2. Macrolides inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. ErythromycinAzithromycin Clarithromycin 3. Tetracyclines inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. Tetracycline Minocycline DoxycyclineLymecycline 4. Fluoroquinolones inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis. Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Enoxacin, Ofloxacin 5. Sulphonamides block bacterial cell metabolism by inhibiting enzymes. Trimethoprim + sulphamethoxazole 6. Aminoglycosides inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. Gentamicin, Amikacin 7. Imidazole antibiotics inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis. Metronidazole 8. The following drugs inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. Fusidic acid, Mupirocin Uses of antibiotics Antibiotics only work against infections caused by bacteria. Bacterial infections are much less common than viral infections. Most coughs and colds are of viral origin so antibiotics should not be prescribed for these. Antibiotics should only use when absolutely necessary, because: 1. There is increasing resistance of bacteria to treatment. 2. Resistant bacteria are selected by the use of antibiotics. 3. Antibiotics may have serious adverse effects on some people. Get in touch with the solution by just clicking the following links- Facebook Group- / solutionpharamcy Mobile App - https://play.google.com/store/apps/de... New Channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) / @pharmacydictionary E-Mail for official and other work - [email protected] #solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #Pharmacognosyvideos #GPAT



![Antibiotic Classes: Mnemonic, Coverage, Mechanism of Action [Pharmacology Made Easy]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_-UHhkIYht4/mqdefault.jpg)




