Скачать с ютуб Class (23) = Introduction to Plant Hormones and its Application | Types & Functions of Plant Hormone в хорошем качестве
Pharmacognosy
Pharmacognosy lecture
plant hormones
phytohormnes
plant growth regulator
auxin
cytokinin
gibberellin
ethylene
abscisic acid
functions of phytohormones
role of plant hormones
application of plant hormones
auxin function
cytokinin function
giberellic acid function
types of plant hormones
tyeps of phytohormones
phytohormones and its function
Phytohormones
Plant hormones
Plant growth regulators
plant hormones and its application
Types of plant hormones
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Class (23) = Introduction to Plant Hormones and its Application | Types & Functions of Plant Hormone в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Class (23) = Introduction to Plant Hormones and its Application | Types & Functions of Plant Hormone или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Class (23) = Introduction to Plant Hormones and its Application | Types & Functions of Plant Hormone в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Class (23) = Introduction to Plant Hormones and its Application | Types & Functions of Plant Hormone
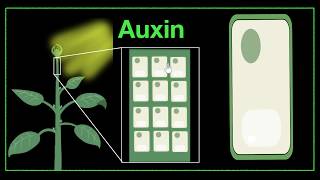
Download "Solution Pharmacy" Mobile App to Get All Uploaded Notes, Model Question Papers, Answer Papers, Online Test and other GPAT Materials - https://play.google.com/store/apps/de... PLANT HORMONES Plant hormones, also known as phytohormones, are chemicals that regulate plant cell processes. They are signal molecules produced within the plant functioning in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of growth and development, from embryogenesi, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and through to reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. The term 'phytohormone' was coined by Went and Thiman and used in the title of their book in 1937. Five major classes: 1.Auxin 2- Cytokinin 3- Abscisic acid 4- ethylene 5- Gibberellins 1. Auxin Auxin is one of the major five plant hormones, mostly present natively as free or conjugated indole-acetic acid (IAA), a tryptophan derivative. Polar auxin transport is tightly regulated, and the hormone has a cardinal role in almost all important processes of a plant's life cycle, such as shoot and root growth, development, cell expansion and division, flowering, fruit maturing, organ patterning, and stress responses. 2. Gibberellins Gibberellins are one of the classical five plant hormones and are diterpenoid weak acids. They are involved in several biological processes in plants such as starch hydrolysis during germination, fruit maturation, and stem elongation. Gibberellin mutants played a key role during the Green Revolution thanks to their sturdier semi-dwarf stature allowing increased yield Cytokinin Cytokinins are one of the classical five plant hormones and are adenine derivatives. Together with auxin, they play an important role in several plant processes such as cell division and differentiation, apical dominance, morphogenesis, and leaf senescence. 3- Ethylene Unlike the other plant hormones, ethylene is a single chemical. It is in the form of a gas at regular temperatures, and allows plants a fast way to communicate between cells and other plantsAs a gas, ethylene quickly diffuses through the fluids of the plant, and can travel through the air. Plants use this hormone to communicate damage to other plants, stimulating them to ripen their fruit or to develop defenses against herbivores. Ethylene induces fruits, nuts, and vegetables to finish growing and to detach from the stem 5- Abscisic Acid The original name of abscisic acid was dormin, because the plant hormones are heavily involved in the dormancy process. Today, these plant hormones have two main recognized functions in plants. First, they regulate the process of seed development. This helps transform the embryo into a fully-fledged seedling. Second, these plant hormones play a crucial role in the plant’s response to temperature and water loss. Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links- Facebook Group- / solutionpharamcy Facebook Page- / pharmavideo New channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) - / @pharmacydictionary Instagram- / solutionpharmacy E-Mail for official and other work - [email protected] LinkedIn- / pushpendrakpatel #solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #GPATonlinetest