Скачать с ютуб Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells | 6/14 | UPV в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells | 6/14 | UPV в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells | 6/14 | UPV или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells | 6/14 | UPV в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells | 6/14 | UPV
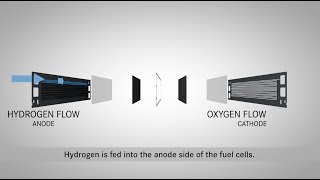
Título: Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Descripción: El objetivo es conocer las características básicas de las pilas basadas en membranas de intercambio protónico, sus componentes y su funcionamiento. Ribes Greus, MD. (2010). Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. http://hdl.handle.net/10251/8165 Descripción automática: In this video, the presenter discusses proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs), highlighting their significance and components including ion-exchange membranes that serve as electrolytes. The focus is on the functionality of the polymeric proton exchange membrane, which separates the anode from the cathode and facilitates the movement of protons, generating electricity. The lecture touches on the operational parameters for PEMFCs, stating the need for low-temperature operation due to polymer degradation at high temperatures. It also discusses the challenge of cell poisoning, necessitating the use of pure hydrogen for oxidation. Furthermore, the presenter explains the cell's structure: the polymeric membrane is sandwiched between the anode and cathode, aided by plates that help in electron transport and gas diffusion. The interface between the membrane and electrodes involves a catalyst layer, typically containing platinum, vital for the electrochemical reactions. Materials for fuel cells are examined, focusing on the proton conductivity offered by sulfonic groups in the polymeric membranes. Also discussed are the porous electrodes that facilitate gas diffusion and the mechanisms through which protons travel across the cell to generate electricity. The video also reviews additional components needed for PEMFC operation, such as Teflon masks and graphite blocks, which serve as current collectors. These elements are crucial for maintaining appropriate water content, vital for proton conductivity, and managing heat within the system. In conclusion, the presenter emphasizes the suitability of PEMFCs for low-temperature applications, offering advantages in lightweight and portability for vehicles and small electronic devices. However, a significant drawback is the need for highly pure hydrogen to avoid catalyst poisoning, potentially raising operational costs. The presenter expresses hope that viewers enjoy the presentation as much as they have. Autor/a: PoliMedia Administrador Curso: Este vídeo es el 6/14 del curso Introduction to Fuel Cells Course | Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV). • Introduction to Fuel Cells Course | U... Universitat Politècnica de València UPV: https://www.upv.es Más vídeos en: / valenciaupv Accede a nuestros MOOC: https://upvx.es #Fuel cells #Proton conductivity #Polymeric membrane #MAQUINAS Y MOTORES TERMICOS




![Как устроены швейные машинки? [Veritasium]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/FFW0GcMCgd0/mqdefault.jpg)


