Скачать с ютуб Piston RING GAP - HOW and WHEN to adjust it + GAP CHART - BOOST SCHOOL #6 в хорошем качестве
piston ring
piston rings
piston ring gap
piston ring gap tool
piston ring gap orientation
piston ring gap chart
piston ring gap calculator
wiseco piston ring gap chart
mahle piston ring gap chart
5 3 stock piston ring gap
piston ring gap spacing
piston ring gap for boost
piston ring gap turbo
piston ring gap supercharger
piston ring filer
engine building
high performance academy
horse power
What is the purpose of piston ring gap?
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Piston RING GAP - HOW and WHEN to adjust it + GAP CHART - BOOST SCHOOL #6 в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Piston RING GAP - HOW and WHEN to adjust it + GAP CHART - BOOST SCHOOL #6 или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Piston RING GAP - HOW and WHEN to adjust it + GAP CHART - BOOST SCHOOL #6 в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Piston RING GAP - HOW and WHEN to adjust it + GAP CHART - BOOST SCHOOL #6
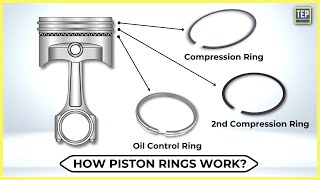
Piston ring filer: https://amzn.to/3v3tz7J AEM ECU: http://bit.ly/D4Ainfinity5 AEM water-meth: https://bit.ly/2zrOkSp?utm_source=D4A... AEM boost controllers: http://bit.ly/D4AtruboostX AEM wideband AFR gauge: http://bit.ly/D4Axserieswb As you know the piston rings play an absolutely key part in your engine they hold combustion pressures in the combustion chamber. In other words they ensure that combustion pushes the piston downward instead of going past the piston. But the very construction of a piston ring is a compromise. Because we can't use rubber bands for piston rings, all piston rings must have a slit or gap in them so that they can be installed and removed from pistons. Of course this gap shouldn't be too large, because then it will let combustion pressures escape through the gap and reduce powder and efficiency. But being too small is an even worse scenario when it comes to piston ring gaps. Other than holding combustion pressure in, piston rings have another key task, and that's to transfer heat from the piston to the cylinder, and then the cylinder transfers heat away to the coolant passing around it. As you know metal, like most things, expands under heat. This means that piston rings also expand under heat. If the ring gap is too small the ring will expand within the limited space of the cylinder, and the rings will eventually run into each other. When this happens the ring will have nowhere left to go and as more heat is introduced the pressure exerted by the ring on the cylinder will increase. This means that more friction will occur between the ring and the cylinder and this will produce even more heat. Eventually the amount of heat will become too high for the ring to transfer it away to the cylinder and coolant. Eventually the piston too will start overheating and by doing so it will start loosing it's structural integrity. This combined to added resistance between the ring and piston means that catastrophic failure is just a matter of time. The most common scenario is broken ring lands and loss of compression together with possible cylinder damage. In any case the engine needs to come out for inspection and likely a rebuild. So what this tell you? Well it tells you that more heat means more ring expansion. If we're rebuilding our engine in it's stock form without significant modifications we don't need to touch the ring gap. But if we modify our engine to introduce more heat into the combustion chamber we need to increase the ring gap to account for this added expansion. Increasing the compression ratio of your engine increases the heat in the combustion chamber because the air and fuel mixture are compressed to a greater extent. The more you compress a gas the closer it's molecules come to each other, the closer they are the more they will contact each other and thus generate friction and heat. We can also add additional heat by significantly increasing the redline of our engine and spending prolonged periods of time at that redline. More engine revolutions means more friction between the rings and the cylinder over the same period of time and thus more heat. But by far the greatest addition of heat into the engine is adding turbocharging or supercharging to a previously naturally aspirated engine or significantly increasing the boost levels in an already turbocharged or supercharged engine. Forced induction stuffs far more air molecules into the same space compared to natural aspiration, which means that it significantly increases the number of molecules in that same space which means that it increases the heat during compression and combustion and thus increases the amount of heat to which the piston rings will be exposed. To account for this, adding forced induction or significantly increasing boost often calls for an adjustment of the piston ring gap. In this video you will find a detailed piston ring gap chart or piston ring gap calculator if you will as well as detailed and simple instructions on how to use a readily available piston ring filing tool. A special thank you to my patrons: Daniel Peter Della Flora Daniel Morgan William Richard Caldwell Pepe Brian Durning Andrew Ruud Brian Alvarez Holset90 D4A merch: https://teespring.com/en-GB/d4a-merch Patreon: / d4a #d4a #boostschool