Скачать с ютуб What Causes Brain Metastases? Chapter 2 — Brain Metastases: A Documentary в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок What Causes Brain Metastases? Chapter 2 — Brain Metastases: A Documentary в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно What Causes Brain Metastases? Chapter 2 — Brain Metastases: A Documentary или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон What Causes Brain Metastases? Chapter 2 — Brain Metastases: A Documentary в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
What Causes Brain Metastases? Chapter 2 — Brain Metastases: A Documentary
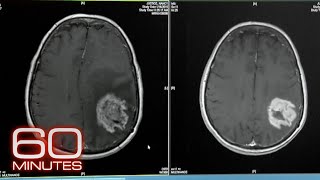
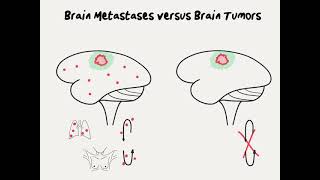
This chapter describes how cancer cells arrive in the brain and turn into brain metastases. Watch the entire documentary from the beginning here: • Brain Metastases: A Documentary | How... There are two types of brain cancer. The first is called primary brain cancer, which originates in the brain and is extremely rare. The second and more common is metastatic brain cancer, which originates elsewhere in the body and travels to the brain. Metastases can develop in the brain when these rogue cells cross the blood-brain barrier. Toxins and other harmful substances are usually filtered out by the blood-brain barrier. Cancer, however, has evolved to penetrate that barrier. Some types of cancer are better at crossing the blood-brain barrier than others. These include melanoma, lung cancer, breast cancer, and testicular cancer. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Video Transcript: David Roberge, MD: There are different kinds of brain tumors. It’s important to discriminate between primary brain cancer, which is a tumor that’s born in the brain, and that’s actually pretty rare. And then there’s metastatic brain cancer, which is five times more common. Part of what makes cancer cancer is that it has the ability to spread throughout the body, so the tumor might start in the breast and it gets to a certain size and it develops some mutations and then a cell will split off, get into the blood, and then stop somewhere in the brain and deposit inside the brain and form other tumors and that would be the process of metastasizing. Orin Bloch, MD: There is a blood-brain barrier and that barrier works very well at keeping toxins and infections and other things floating around through our blood out of the brain. But cancer has developed a mechanism which it can penetrate that barrier and certain cancers in particular are better at penetrating it than others, which is why we tend to see most metastatic tumors from lung cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, and testicular cancer. If you remove one of these metastatic tumors from the brain with surgery and you look at it under a microscope, it looks like the cancer from the original source. So a breast cancer metastasis looks like abnormal breast tissue rather than brain tissue. They are growing into a ball of cells that is the cancer, but they’re not incorporating themselves into the brain. They are unwanted neighbors, if you will. Douglas Kondziolka, MD: Our goal is to find those tumors early because as the tumors get bigger, the success rates drop. Typically with radiosurgery people have quoted success rates at stopping a brain tumor in the range of 85%, so when we say how do we get that to 95%, to 98%, to 99%? It’s with identifying the tumors earlier and that means getting a periodic brain scan to check, because missing a brain tumor, if it grows, can cause neurologic symptoms that we’d like to avoid. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Interested in learning more? See our other chapters below that address many questions regarding brain metastases: What are brain metastases? • What are Brain Metastases? Chapter 1 ... What are the possible treatment options for brain metastases? • Is Chemotherapy Effective for Brain M... What is Whole Brain Radiation Therapy (WBRT) and how is it used to treat brain metastases? • What is Whole Brain Radiation Therapy... What is stereotactic radiosurgery? • What is Stereotactic Radiosurgery? Ch... What is the Gamma Knife? • What is the Gamma Knife? Chapter 6 — ... What is a linear accelerator and how does it work? • What is a Linear Accelerator? Chapter... Frame-based vs. frameless radiosurgery. What’s the difference and how does it impact the patient and treatment? • How are Patients Immobilized During R... How does Cyberknife technology treat brain tumors? • What is the CyberKnife? Chapter 9 — B... What is a multileaf collimator and what role does it play in shaping radiation for radiosurgery? • What is Shaped Beam Radiosurgery? Cha... What if a patient has more than one brain metastases? How are they treated? • Can Multiple Tumors Be Treated at the... Some radiosurgery treatments can be completed in just one visit. Why are multiple treatments (known as fractions) sometimes necessary? • When is Radiosurgery Performed More t... If it can harm the patient, why is Whole Brain Radiation Therapy (WBRT) still done? • Why is Whole Brain Radiation Therapy ... What does “Cancer is being treated as a chronic illness" mean? How do brain metastases patients maintain their quality of life? • What Happens After Radiosurgery? Chap... Why is surgery sometimes necessary to treat brain metastases? • When is Surgery Recommended? Chapter ... How do I choose the best care team for treating my brain metastases? • How to Choose the Best Radiosurgery T... What is the future outlook a brain metastases diagnosis? • What is the Future of Brain Metastase...