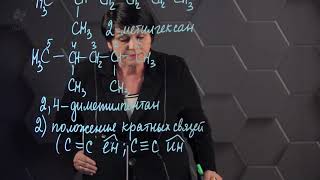Скачать с ютуб Carbon and its Compounds || class 10 || one shot || Complete chapter in 26 mins в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Carbon and its Compounds || class 10 || one shot || Complete chapter in 26 mins в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Carbon and its Compounds || class 10 || one shot || Complete chapter in 26 mins или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Carbon and its Compounds || class 10 || one shot || Complete chapter in 26 mins в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Carbon and its Compounds || class 10 || one shot || Complete chapter in 26 mins
@YesBio @YesAcademy7 @Yesbio.travel #carbonanditscompoundsclass10 #carbonanditscompound #class10science #carbonanditscompounds Download the app for live interacting classes at best possible prices, recorded videos of live classes, DPPS, chapter wise test, mock test and live doubt solving sessions. #biology #neet #neetbiology #cbse Download the app!!! https://tdgdof.on-app.in/app/home?org... Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/bindiya.goel... Instagram: https://instagram.com/bindiyaamit7?ig... Another you tube channel: / @yesacademy7 Chemical substances containing carbon are referred to as carbon compounds. Except for hydrogen, there are more carbon compounds than any other chemical element. Compounds of carbon with double bonds and triple bonds are called unsaturated compounds, while those with carbon-carbon single bonds are called saturated compounds. Covalent Bonding Difficulty of Carbon to Form a Stable Ion To achieve the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas, He, if the carbon atom loses four of its valence electrons, a huge amount of energy is involved. C4+ ion hence formed, will be highly unstable due to the presence of six protons and two electrons. If the carbon atom gains four electrons to achieve the nearest electronic configuration of the noble gas, Ne, C4− ion will be formed. But again, a huge amount of energy is required. Moreover, in C4+ ions it is difficult for 6 protons to hold 10 electrons. Hence, to satisfy its tetravalency, carbon shares all four of its valence electrons and forms covalent bonds. Ionic Bond Ionic bonding involves the transfer of valence electron/s, primarily between a metal and a nonmetal. The electrostatic attractions between the oppositely charged ions hold the compound together. Ionic compounds: Are usually crystalline solids (made of ions) Have high melting and boiling points Conduct electricity when melted Are mostly soluble in water and polar solvents Covalent Bond A covalent bond is formed when pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. It is primarily formed between two same nonmetallic atoms or between nonmetallic atoms with similar electronegativity. To know more about Covalent Bonds, visit here. Lewis Dot Structure Lewis structures are also known as Lewis dot structures or electron dot structures. These are basically diagrams with the element’s symbol in the centre. The dots around it represent the valence electrons of the element. Covalent Bonding in H2, N2 and O2 Formation of a single bond in a hydrogen molecule: Each hydrogen atom has a single electron in the valence shell. It requires one more to acquire the nearest noble gas configuration (He). Therefore, both the atoms share one electron each and form a single bond. Formation of a double bond in an oxygen molecule: Each oxygen atom has six electrons in the valence shell (2, 6). It requires two electrons to acquire the nearest noble gas configuration (Ne). Therefore, both the atoms share two electrons each and form a double bond. Formation of a triple bond in a nitrogen molecule: Each nitrogen atom has five electrons in the valence shell (2, 5). It requires three electrons to acquire the nearest noble gas configuration (Ne). Therefore, both atoms share three electrons each and form a triple bond.