РЎРәР°СҮР°СӮСҢ СҒ СҺСӮСғРұ Streptococcus Pneumoniae : Case presentation РІ С…РҫСҖРҫСҲРөРј РәР°СҮРөСҒСӮРІРө
streptococcus pneumoniae
streptococcus pneumoniae disease
meningitis/ bacterial /streptococcus pneumoniae
streptococcus pneumoniae pathogenesis
streptococcus pneumoniae infection
streptococcus pneumoniae lab diagnosis
streptococcus pneumoniae clinical features
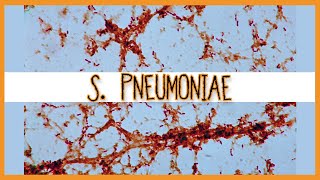
streptococcus pneumoniae microbiology
streptococcus pneumoniae treatment
streptococcus pneumoniae diagnosis
streptococcus pneumoniae microbiologГӯa
streptococcus
pneumonia
bacterial pneumonia
pneumonia symptoms
nmc
РЎРәР°СҮР°СӮСҢ РұРөСҒРҝлаСӮРҪРҫ Рё СҒРјРҫСӮСҖРөСӮСҢ СҺСӮСғРұ-РІРёРҙРөРҫ РұРөР· РұР»РҫРәРёСҖРҫРІРҫРә Streptococcus Pneumoniae : Case presentation РІ РәР°СҮРөСҒСӮРІРө 4Рә (2Рә / 1080p)
РЈ РҪР°СҒ РІСӢ РјРҫР¶РөСӮРө РҝРҫСҒРјРҫСӮСҖРөСӮСҢ РұРөСҒРҝлаСӮРҪРҫ Streptococcus Pneumoniae : Case presentation или СҒРәР°СҮР°СӮСҢ РІ РјР°РәСҒималСҢРҪРҫРј РҙРҫСҒСӮСғРҝРҪРҫРј РәР°СҮРөСҒСӮРІРө, РәРҫСӮРҫСҖРҫРө РұСӢР»Рҫ загСҖСғР¶РөРҪРҫ РҪР° СҺСӮСғРұ. ДлСҸ СҒРәР°СҮРёРІР°РҪРёСҸ РІСӢРұРөСҖРёСӮРө РІР°СҖРёР°РҪСӮ РёР· С„РҫСҖРјСӢ РҪРёР¶Рө:
ЗагСҖСғР·РёСӮСҢ РјСғР·СӢРәСғ / СҖРёРҪРіСӮРҫРҪ Streptococcus Pneumoniae : Case presentation РІ С„РҫСҖРјР°СӮРө MP3:
Р•СҒли РәРҪРҫРҝРәРё СҒРәР°СҮРёРІР°РҪРёСҸ РҪРө
загСҖСғзилиСҒСҢ
РқРҗР–РңРҳРўР• ЗДЕСЬ или РҫРұРҪРҫРІРёСӮРө СҒСӮСҖР°РҪРёСҶСғ
Р•СҒли РІРҫР·РҪРёРәР°СҺСӮ РҝСҖРҫРұР»РөРјСӢ СҒРҫ СҒРәР°СҮРёРІР°РҪРёРөРј, РҝРҫжалСғР№СҒСӮР° РҪР°РҝРёСҲРёСӮРө РІ РҝРҫРҙРҙРөСҖР¶РәСғ РҝРҫ Р°РҙСҖРөСҒСғ РІРҪРёР·Сғ
СҒСӮСҖР°РҪРёСҶСӢ.
РЎРҝР°СҒРёРұРҫ Р·Р° РёСҒРҝРҫР»СҢР·РҫРІР°РҪРёРө СҒРөСҖРІРёСҒР° savevideohd.ru
Streptococcus Pneumoniae : Case presentation
рҹ“Ң рқҗ…рқҗЁрқҗҘрқҗҘрқҗЁрқҗ° рқҗЁрқҗ§ рқҗҲрқҗ§рқҗ¬рқҗӯрқҗҡрқҗ рқҗ«рқҗҡрқҗҰ:- В В /В drgbhanuprakashВ В рҹ“Ңрқ—қрқ—јрқ—¶рқ—» рқ—ўрқҳӮрқ—ҝ рқ—§рқ—Ірқ—№рқ—Ірқ—ҙрқ—ҝрқ—®рқ—ә рқ—–рқ—өрқ—®рқ—»рқ—»рқ—Ірқ—№ рқ—ӣрқ—Ірқ—ҝрқ—І:- https://t.me/bhanuprakashdr рҹ“Ңрқ—ҰрқҳӮрқ—ҜрқҳҖрқ—°рқ—ҝрқ—¶рқ—Ҝрқ—І рқ—§рқ—ј рқ— рқҳҶ рқ— рқ—®рқ—¶рқ—№рқ—¶рқ—»рқ—ҙ рқ—ҹрқ—¶рқҳҖрқҳҒ:- https://linktr.ee/DrGBhanuprakash Overview of Streptococcus Pneumoniae ________________________________________ Characteristics: Streptococcus pneumoniae, also known as pneumococcus, is a gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic bacterium. It is often found in pairs (diplococci) and is known for its polysaccharide capsule, which is key to its virulence. Habitat: Commonly resides in the human nasopharynx, often without causing harm. However, it can become pathogenic, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions. Pathogenesis of Pneumonia ____________________________ Transmission: Typically spreads via respiratory droplets. Infection occurs when the bacteria are inhaled into the lungs. Invasion and Inflammation: Once in the lungs, the bacteria's capsule helps evade the host's immune response, allowing it to adhere to and invade the alveolar epithelium. Immune Response: The body responds with an inflammatory reaction. White blood cells, particularly neutrophils, are recruited to the site, leading to the characteristic symptoms of pneumonia. Clinical Features _________________ Symptoms: Common symptoms include cough (often producing rust-colored sputum), fever, chills, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Diagnosis: Diagnosis is typically made through chest X-rays, sputum cultures, and blood tests. Treatment and Management ____________________________ Antibiotics: Penicillin is traditionally the first-line treatment. However, antibiotic resistance is a growing concern, necessitating alternative antibiotics in some cases. Supportive Care: Includes oxygen therapy for patients with respiratory distress and fluid management. Prevention Strategies ______________________ Vaccination: Pneumococcal vaccines are a critical component in preventing Streptococcus pneumoniae infections. There are two types: pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23). Hygiene Practices: Regular hand washing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can reduce the risk of transmission. Complications _______________ Pleural Effusion: Occurs when fluid accumulates in the pleural space. Bacteremia and Sepsis: Bacteria can enter the bloodstream, leading to a more systemic and potentially life-threatening infection. Meningitis: In rare cases, the bacteria can infect the meninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Epidemiology and Public Health Impact Incidence and Prevalence: Commonly affects children and the elderly. It's a leading cause of bacterial pneumonia worldwide. Public Health Measures: Surveillance and vaccination programs are vital for controlling outbreaks and reducing the disease burden. Pathophysiology _________________ Host Defense Mechanisms: The bodyвҖҷs immune system, particularly the mucociliary clearance mechanism and phagocytic activity, initially acts to eliminate the bacteria. However, the capsule of Streptococcus pneumoniae can inhibit these defenses. Bacterial Virulence Factors: The capsule is the primary virulence factor, preventing phagocytosis. Other factors include pneumolysin, which damages ciliated epithelial cells and white blood cells. #fmge #fmgevideos #rapidrevisionfmge #fmgejan2023 #mbbslectures #nationalexitexam #nationalexittest #neetpg #usmlepreparation #usmlestep1 #fmge #usmle #drgbhanuprakash #medicalstudents #medicalstudent #medicalcollege #neetpg2023 #usmleprep #usmlevideos #usmlestep1videos #medicalstudents #neetpgvideos #pneumonia #streptococcuspneumoniae #streptococcus