Скачать с ютуб Simple Genetic Cross Example Using Punnett Squares в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Simple Genetic Cross Example Using Punnett Squares в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Simple Genetic Cross Example Using Punnett Squares или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Simple Genetic Cross Example Using Punnett Squares в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Simple Genetic Cross Example Using Punnett Squares
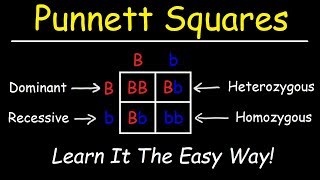
Learn more about Punnet Squares here: • Punnett Square Basics | Mendelian Gen... Learn more about Alleles here: • Homozygous vs Heterozygous Alleles | ... Learn more about Genotypes and Phenotypes here: • Genotype vs Phenotype | Understanding... Let’s solve a simple genetic cross using a Punnett square. In rabbits, coat color is determined by a single gene with two alleles: uppercase B (brown coat) and lowercase b (white coat). A homozygous dominant brown-coated rabbit (BB) is crossed with a homozygous recessive white-coated rabbit (bb). Determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring. To start, let’s set up our Punnett square. We will put the brown-coated rabbit alleles across the top. Both uppercase B. And the white-coated rabbit on the side. Both lowercase b. Now we match up the alleles in their corresponding squares. In this case, every square gets one big B and one little b. So these are the possible outcomes, and the question asked for the possible genotypes and phenotypes. Genotypes are the alleles, which are 100% heterozygous, big B and little b. The phenotype refers to the expression of the genes. Given that there is only one genotype, we only have one phenotype, brown-coated rabbits.