Скачать с ютуб Cell - A Unit of Life | ICSE Class 9 Biology | Cell Organelles, Nucleus, Protoplasm в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Cell - A Unit of Life | ICSE Class 9 Biology | Cell Organelles, Nucleus, Protoplasm в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Cell - A Unit of Life | ICSE Class 9 Biology | Cell Organelles, Nucleus, Protoplasm или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Cell - A Unit of Life | ICSE Class 9 Biology | Cell Organelles, Nucleus, Protoplasm в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Cell - A Unit of Life | ICSE Class 9 Biology | Cell Organelles, Nucleus, Protoplasm
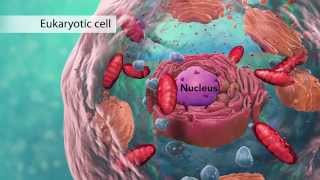
IAS Preparation: https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/IAS/ NET Preparation: https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/UGC/ CUET UG: https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/C... Exam Preparation - https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/ icse biology class 9 concise biology class 9 selina biology class 9 selina class 9 biology selina concise biology class 9 concise biology class 9 icse biology selina class 9 selina biology 9 biology concise class 9 selina biology class 9 icse icse 9 biology srijan biology class 9 introducing biology class 9 icse icse concise biology class 9 conscience biology class 9 candid icse biology class 9 selina publishers biology for clas concise selina biology class 9 icse selina biology class 9 srijan icse biology class 9 biology class 9 selina Masters Level topics: / testprep NCERTs: / examrace Hindi Lectures: / examracehindi Kids & Olympiads: / funprof Our Websites https://www.examrace.com https://www.doorsteptutor.com https://www.flexiprep.com https://www.examtestprep.com https://www.jobduniya.com #upscpreparation #iasprelims2023 #howtoqualifyias #iaspreparationstrategy #doorsteptutor #netpaper1 #ugcnetpreparation #howtoqualifyJRF #cell #icseclass9 #icsebiology Hooke examined cork cells under microscope - honeycomb like structure as cells – empty spaces of dead cells surrounded by cellulose wall as seen by Hooke. Cell denotes living content or protoplast Simple microscope by Anton van Leeuwenhoek – tiny biconvex lens b/w brass plates – magnification of 75 to 250 times Light or Compound microscope – using 2 lenses to achieve greater magnified view – light from oil flame was thrown on object placed on stage below using convex mirror Modern complex microscope is optical – used in science laboratories – eyepiece lens provides further magnification after objective lens – can magnify upto 1500 times. Electron microscope – Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll -magnify upto 40,000 times to 2 lakh times – can show 3-D images. Beam focus on electromagnets and project on fluorescent screen by making virtual image. 1885 Rudolf Virchow – Omnis cellula-e-cellula – cells arise form pre-existing cells Virus – exception as it is connecting link between living and non-living. They are hereditary material enclosed in protein coat. Protoplasm and nucleus are absent. DNA/RNA is genetic material. New born baby – 2 trillion cells Adult human being – 37.2 trillion cells; 25,000 to 30,000 RBC; 30 million WBC; 10000 million nerve cells Single celled algae – Acetabularia – 10cm in height; fiber cell of Manila Hemp -100 cm Cells remain small in size as small cells provides more surface area per unit volume – one 4cm cube – surface area is 16 sq cm while eight 2 cm cell surface area is 32 sq cm Benefits of small size – better communication, better diffusion of nutrients, greater diffusion of metabolic waste, greater diffusion of respiratory gases; any damage to cell can be easily repaired Human WBC are amoeboid RBC are circular and biconcave Muscle cell – long and contractile Xylem – elongated and tubular for conduction of water Guard cells – kidney shaped to open and close stomatal aperture for gaseous exchange 10000 mycoplasma in a row are as wide as human hair diameter Prokaryotic – bacteria, cyanobacteria – acellular, no well defined nucleus, naked DNA, single circular chromosome; small scattered ribosome; nuclear membrane, golgi complex absent; Dna found in nucleoid; cell range is 1-10 micron Eukaryotic – both unicellular and multicellular – in all living organisms, nucleus present; DNA with protein as chromatin fiber; multiple linear chromosome; bigger ribosome attached or free to ER; nuclear membrane, golgi complex present Plant cell – cell wall present; centrosome absent; vacuole large; plastids present; lysosome absent; stored food as starch; cytoplasm is thin and pushed to periphery; simple golgi complex as dictyosome scattered in cytoplasm; nucleus pushed towards periphery Animal cell – cell wall absent; centrosome present; vacuoles small and many; plastids absent; lysosome present; food stored as glycogen; cytoplasm fills entire cell & is dense; golgi complex near nucleus and elaborate; nucleus is at center Double membrane – ER, Mitochondria, plastid, vacuole, golgi bodies Single membrane – lysosome Non-membranous – ribosome; centrosome; centrioles