Скачать с ютуб Receptors and Second Messenger system; G-protein, Enzyme linked and Ligand gated ion channels в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Receptors and Second Messenger system; G-protein, Enzyme linked and Ligand gated ion channels в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Receptors and Second Messenger system; G-protein, Enzyme linked and Ligand gated ion channels или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Receptors and Second Messenger system; G-protein, Enzyme linked and Ligand gated ion channels в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Receptors and Second Messenger system; G-protein, Enzyme linked and Ligand gated ion channels
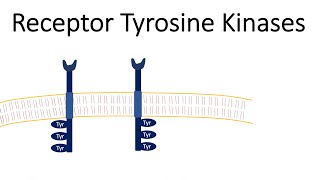
There are four major transmembrane signalling systems: Ligand gated channels, G protein coupled receptors, Enzyme linked receptors, and intracellular receptors Ligands, usually neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine Cross the neuromuscular junction synaptic cleft To bind to their nicotinic receptors which are linked to ion channels Activation of nicotinic receptors induces conformational changes that results in opening of ion channels That allow the influx of various ions For example, sodium ions which modulate the cellular action potential. Second type is G protein Coupled receptors In this type of signalling Binding of the ligand to its extracellular binding site induces conformational change in the transmembrane receptor This conformational change results in activation of α subunit of G protein Activation of α subunit results in dissociation of GDP and binding of GTP to α subunit Binding of GTP to α subunit stimulates its dissociation from β and γ subunits which form separate βγ dimer Then both α subunit and βγ dimer activate various effector targets For example, α subunit activates membrane bound enzymes such as Adenylyl cyclase and Phospholipase C which in turn Activate cascade of second messenger reactions Which leads to various biological responses Third type is Enzyme linked receptors For example, insulin receptors Where binding of insulin to the extracellular domain of the receptors Stimulate conformational change That results in phosphorylation and activation of tyrosine kinase enzyme which is part of the intracellular domain And this the main difference between enzyme linked receptors and G protein coupled receptors As tyrosine kinase is innate and intrinsic part of the receptor and not detached from it during activation Then active phosphorylated tyrosine kinase phosphorylates effector protein called Insulin receptor substrate abbreviated as IRS Which in turn stimulates cascade of wide biological responses Finally Intracellular receptors The lipophilic molecules such as steroid hormones Pass through cell membrane and bind to and activate their intracellular receptors The activated internal receptors regulate the expression of various genes