Скачать с ютуб Refrigerant Pressure Details | Animation | в хорошем качестве
Refrigerant Pressure
Refrigeration Systems
HVAC (Heating
Ventilation
and Air Conditioning)
Pressure-Temperature Relationship
Refrigerant Phase Change
Refrigerant Safety
System Pressure Control
Refrigerant Types
Heat Transfer in Refrigeration
Refrigerant Cycle
Refrigerant Management
Refrigerant Properties
Cooling Systems
Refrigerant Troubleshooting
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Refrigerant Pressure Details | Animation | в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Refrigerant Pressure Details | Animation | или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Refrigerant Pressure Details | Animation | в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Refrigerant Pressure Details | Animation |
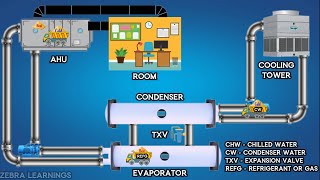
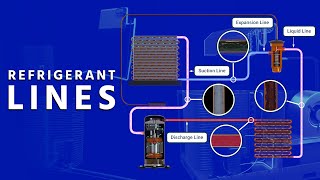
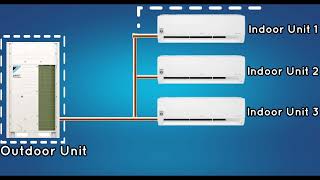
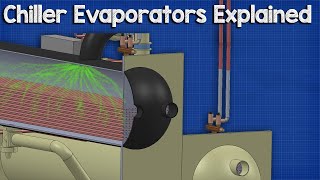
Refrigerant pressure is a crucial aspect of refrigeration and air conditioning systems, as it plays a fundamental role in the operation of these systems. Refrigerants are substances used to transfer heat from one location to another within a refrigeration cycle. They undergo phase changes from a low-pressure vapor to a high-pressure liquid and back to vapor as they circulate through the system. Here are some key points about refrigerant pressure: Pressure-Temperature Relationship: In a closed refrigeration system, the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant are closely related. When the pressure increases, so does the temperature, and vice versa. This relationship is described by the ideal gas law, which is an approximation for most refrigerants under typical operating conditions. Low and High-Side Pressures: Refrigeration systems typically have both a low-pressure side (the evaporator and the suction line leading to the compressor) and a high-pressure side (the condenser and the discharge line from the compressor). The pressure levels on these sides are carefully controlled to ensure efficient heat transfer and system operation. Safety: Proper control of refrigerant pressures is essential for the safe operation of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Excessive pressure can lead to equipment failure or even catastrophic accidents, such as refrigerant leaks or explosions. Refrigerant Types: Different refrigerants have different pressure-temperature relationships, which is one of the factors that determine their suitability for specific applications. Refrigerant selection must take into account the desired temperature range and system pressure levels. In summary, refrigerant pressure is a critical parameter in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, governing the phase changes and heat transfer processes that enable these systems to cool or heat spaces and maintain the desired temperature conditions. Proper pressure control and maintenance are essential for efficient and safe system operation.