Скачать с ютуб Deciphering Immuno-oncology: Targeting Innate Immunity in Cancer в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Deciphering Immuno-oncology: Targeting Innate Immunity in Cancer в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Deciphering Immuno-oncology: Targeting Innate Immunity in Cancer или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Deciphering Immuno-oncology: Targeting Innate Immunity in Cancer в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Deciphering Immuno-oncology: Targeting Innate Immunity in Cancer
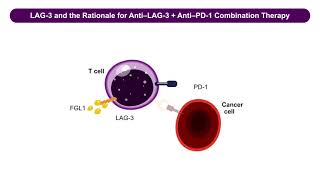
Participating Experts: Stefani Spranger, PhD (MIT) and Santiago Zelenay, PhD (Cancer Research UK) ⬇️ Expand “Show More” to view abstract and table of contents Explore/download the Cell-Intrinsic Innate Immunity Signaling Pathway Diagram: https://cst-science.com/mz55z2 While targeting T cells has proven to be a technically successful treatment protocol for most cancer immunotherapies, only a fraction of cancer patients respond to these interventions. Of late there has been a surge of interest in investigating the relatively underexplored innate immune system as a possible tool for therapeutic intervention. Innate immune effector cells, including natural killer cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells, have been shown to interact with cancers and inhibit their progression. Dissecting the molecular details of these interactions will aid in identifying cancer-derived intrinsic factors that can be exploited to be develop effective immunotherapy regimens. In this webinar recording, the speakers provide examples of how innate immunity pathways are involved in fighting cancer, and how these pathways might be co-opted to generate new treatments. Table of Contents: 0:43 Welcome and overview 2:56 Santiago Zelenay speaker profile 3:32 Manipulating inflammation to raise cancer immunogenicity 5:07 How tumors evade immune responses: a longstanding question 6:48 Dual role of inflammation in cancer 8:50 Mutant Braf-driven melanoma cells from progressively growing tumours in WT mice 9:42 Innate immune cells are essential for initiating adaptive immunity 10:48 Conditioned medium from Braf(V600E) melanoma cells has profound modulatory effects on dendritic cells 13:25 Braf(V600E) melanoma cells produce PGE2 via COX-2 and COX-1 14:49 COX-dependent melanoma growth through evasion of immunity 20:04 Manipulating inflammation to raise cancer immunogenicity 20:46 Cyclooxygenase-inhibition synergizes with PD-1 blockade 23:23 A COX-2 dependent inflammatory signature is conserved in human cancers 24:52 Conclusions and implications 26:38 Stephani Spranger speaker profile 27:27 The relationship between Batf3-DC and anti-tumor T-cell responses 25:54 CD8+ T cell inflammation is associated with an increased response to checkpoint blockade therapy 29:31 Anti-PD-1 therapy appears to be preferentially effective in T cell-inflamed tumors 31:00 Identification of pathways differentially activated between T cell-inflamed and non-T cell-inflamed patients 32:50 Genetically engineered mouse tumors lack T cell infiltration 34:40 CTLA-4/PD-L1 checkpoint blockade fails to control beta-catenin-expressing tumors 34:41 Non-T cell-inflamed tumors have reduced numbers of Batf3-DC 37:13 Lack of CD103+ DC is associated with reduced priming of tumor-specific T cells 38:19 CD103+ DC are essential for T cell priming 40:24 Tumors lacking Batf-3 DC show reduced 2C T cell numbers 45:00 Are Batf3-DC within the tumor required for recruitment of effector T cells? 46:40 CD103+ DC are essential for effector T cell recruitment and T cell priming 48:01 Questions and Answers About CST®: Cell Signaling Technology (CST) is a private, family-owned company, founded by scientists and dedicated to providing high-quality research tools to the biomedical research community. Our employees operate worldwide from our U.S. headquarters in Massachusetts, and our offices in the Netherlands, China, and Japan. https://cellsignal.com/about Cell Signaling Technology and CST are registered trademarks of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. #antibody #CSTWebinar



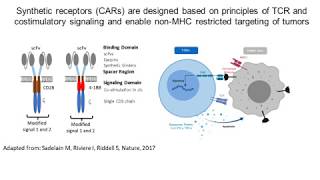
![Tumor microenvironment in a nutshell [WEBINAR]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/UWMJMLpDh0E/mqdefault.jpg)