Скачать с ютуб Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) - Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) - Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) - Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) - Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) - Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
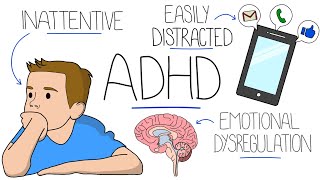
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, also known as ADHD, is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, distractibility, and sometimes, hyperactivity. There are three types of ADHD. Inattentive. Hyperactive-impulsive. And combined. Out of these three, the combined type is more common. Since the diagnosis of ADHD is primarily clinical, signs and symptoms themselves become the diagnostic criteria. So, let’s discuss them together. Diagnostic criteria based on the symptoms of inattention include the following. First, individuals with ADHD don’t pay close attention to details or make careless mistakes. They have difficulty sustaining attention. They don’t seem to listen when spoken to directly. They don’t follow instructions and fail to finish tasks such as homework. They have difficulty in organizing tasks and activities. They dislike or avoid being part of tasks that require sustained mental efforts. They lose things that are required for tasks, such as pencils and books. They are often easily distracted by external stimuli like music. And finally, they are usually forgetful in daily activities. Children who have at least 6 out of the above 9 features are considered to have ADHD. In adolescents and adults, the presence of five features is enough to make a diagnosis. Diagnostic criteria based on hyperactive-impulsive symptoms include the following. Individuals with ADHD often fidget, and they tap their hands or feet, or squirm in their seat. They spontaneously get up in situations where remaining seated is expected. They run around or climb when inappropriate. They don’t usually play or have fun quietly. They cannot stay still for a long time. They talk excessively. They give answers to questions before a question has been fully asked. They have difficulty waiting for their turn. And they often interrupt others. Children who have at least 6 out of the above 9 features are considered to have ADHD. In adolescents and adults, the presence of five features is enough to make a diagnosis. It is important to note that these symptoms usually appear before 12 years of age, in at least 2 settings, such as school and home. The exact cause of ADHD is unclear. However, genetics plays a substantial role. Studies indicate that neurotransmitters such as dopamine and noradrenaline are involved in the pathogenesis. Frontal, and prefrontal cortex, parietal lobe, and the cerebellum are the regions of the brain that are mainly affected. Studies show structural and functional changes in these regions, including deformations in basal ganglia. ADHD is associated with several other psychiatric illnesses. For example, many individuals have both ADHD and antisocial personality disorder. These individuals are at a higher risk of causing harm to themselves and others. ADHD is also linked to addiction. Some individuals have both ADHD and autism. Finally, treatment of ADHD involves a multimodal approach, which includes medical therapy, behavioral psychotherapy, psychosocial interventions, and cognitive therapy. First-line medical therapy of ADHD is stimulants, which include methylphenidate and dextroamphetamine. These medications should be started at the lowest effective dose, and adjustments can be made depending on the clinical response. #adhd #medtoday adhd,attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,adhd symptoms,adhd diagnostic criteria,adhd diagnosis,adhd treatment,attention deficit disorder,adhd causes,adhd pathogenesis,adhd lecture,adhd psychiatry,adhd & autism