Скачать с ютуб Concentration and Molarity explained: what is it, how is it used + practice problems в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Concentration and Molarity explained: what is it, how is it used + practice problems в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Concentration and Molarity explained: what is it, how is it used + practice problems или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Concentration and Molarity explained: what is it, how is it used + practice problems в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Concentration and Molarity explained: what is it, how is it used + practice problems
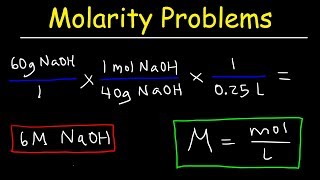
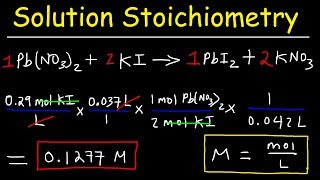
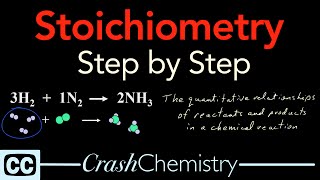
What is concentration, how does molarity measure concentration, and how can we use molarity in calculations to find specific amounts of ingredients to make solutions of a specific volume and concentration? This video includes four practice problems on how to calculate molarity and how to use molarity to find specific amounts of solute or volume to be used for a needed concentration (molarity). There are also sporadic non-sequiturs, both verbal and visual, to add some enormous levity to the proceedings, for the approbation of all concerned. CC Academy videos are easy 101 crash course tutorials for step by step Chemistry help on your chemistry homework, problems, and experiments: - Solution Stoichiometry Tutorial: How to use Molarity - Stoichiometry - Quantum Numbers - Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment, Explained - Covalent Bonding Tutorial: Covalent vs. Ionic bonds - Metallic Bonding and Metallic Properties Explained: Electron Sea Model - Effective Nuclear Charge, Shielding, and Periodic Properties - Electron Configuration Tutorial + How to Derive Configurations from Periodic Table - Orbitals, the Basics: Atomic Orbital Tutorial — probability, shapes, energy - Metric Prefix Conversions Tutorial - Gas Law Practice Problems: Boyle's Law, Charles Law, Gay Lussac's, Combined Gas Law - Ionic Bonds and Compounds - Chemical reaction types - product prediction for specific reaction types - Surface Tension - what is heat - what is fire - The Bohr Model of the Atom - Organic Molecules and the Versatility of Carbon - Hybrid Orbitals-- Valence Bond Theory - Ideal Gas Law and Gas Density