Скачать с ютуб Testicular Torsion, Understand this severe pain в хорошем качестве
Testicular torsion
spermatic cord
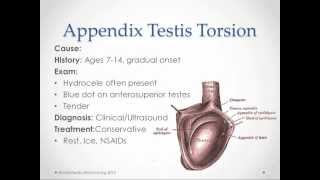
bell-clapper deformity
scrotal pain
testicle swelling
abdominal pain
nausea
vomiting
scrotal discoloration
testicle positioned higher
Doppler ultrasound
physical examination for testicular torsion
manual detorsion
emergency surgery
orchiopexy
orchiectomy
infertility risk
testicle atrophy
trauma-induced testicular torsion
pain during urination
psychological impact of torsion
testicle loss
testicular self-examination
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Testicular Torsion, Understand this severe pain в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Testicular Torsion, Understand this severe pain или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Testicular Torsion, Understand this severe pain в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Testicular Torsion, Understand this severe pain
Testicular Torsion: Overview, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment *Introduction* Testicular torsion is a medical emergency where the spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testicle, twists. This twisting restricts blood flow, leading to severe pain and swelling. Without prompt treatment, it can result in permanent damage to the affected testicle or even require its removal. --- *Causes and Risk Factors* **Congenital abnormalities**: A condition called the "bell-clapper deformity" allows testicles to move more freely, increasing the risk of torsion. **Age**: Most common during adolescence (12-18 years old), but it can occur at any age. **Injury**: Trauma to the testicles may trigger torsion. **Cold temperatures**: Rapid temperature changes can occasionally induce torsion. **Family history**: Genetic predisposition may increase the risk. --- *Symptoms* **Severe testicular pain**: Sudden and sharp pain in the scrotum. **Scrotal swelling**: The affected side may become enlarged. **Abdominal pain**: Particularly in younger boys. **Nausea and vomiting**. *Testicle positioned higher than usual* or at an unusual angle. *Pain during urination* (though less common). *Redness or discoloration* of the scrotum. --- *Diagnosis* **Physical examination**: The doctor checks for tenderness, swelling, and abnormal testicle position. **Ultrasound with Doppler imaging**: Evaluates blood flow to the testicles, which is usually reduced in torsion cases. **Urine tests**: To rule out infections. **Manual detorsion**: Sometimes, doctors attempt to untwist the spermatic cord manually to relieve symptoms. --- *Treatment* **Emergency surgery (orchiopexy)**: The twisted testicle is untwisted, and both testicles are secured to prevent future torsion. **Orchiectomy**: If the blood supply has been compromised for too long, the affected testicle may need to be removed. **Pain management**: Painkillers are provided post-surgery. **Monitoring**: Follow-up care ensures no recurrence or complications. --- *Prognosis and Complications* Early intervention, ideally within 6 hours, often preserves testicle function. If untreated, prolonged lack of blood flow can lead to: **Infertility**: If both testicles are affected or removed. **Testicle atrophy**: Shrinking of the affected testicle due to damage. **Psychological impact**: Loss of a testicle can affect mental health. Testicular torsion is a time-sensitive condition. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking immediate medical attention can save the testicle and prevent complications. Regular self-examinations may also help detect abnormalities before they escalate.