Скачать с ютуб Antibodies (Everything you NEED to know) +TABLE - Immunology в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Antibodies (Everything you NEED to know) +TABLE - Immunology в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Antibodies (Everything you NEED to know) +TABLE - Immunology или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Antibodies (Everything you NEED to know) +TABLE - Immunology в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Antibodies (Everything you NEED to know) +TABLE - Immunology
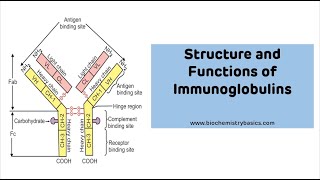
This video is part 2 of Acquired immunity - Antibodies Content 0:00 Introduction 0:06 Where do Antibodies Come From? 5:31 Components of an Antibody 7:32 Domains 8:37 IgG 9:50 IgM 11:53 IgA 13:39 IgD 14:22 IgE 15:17 Differences Between Antibodies 15:56 Table to Memorize ------------------------------- 🫀 Join: / @taimtalksmed 📷 Follow my IG: / taimtalksmed 💝 Donation link: https://www.buymeacoffee.com/taimtalk... ------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- All information in my immunology videos are from: - Book: Immunology, Eighth Edition by David Male, Jonathan Brostoff, David Roth and Ivan Roitt - Additional research in PubMed - University lecture materials -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Antibodies: Plasma proteins Where they come from: 1. B-cell (with BCR - IgG/D) bind to antigen 2. Present it on MHC II 3. APC activates a naive Th cell through TCR (CD4 and CD3), B7/CD28 and IL-4 receptor 4. Naive T helper cell secretes IL2 (autocrine) 5. Becomes an active Th2 6. Th2 helps active B-cell through CD40L/CD40 and T cell receptor. 7. IL-4, IL-5, IL-8, IL-10, IL-2, IFN gamma released depending on what type of antibody is needed. Components of an Antibody: Has: Light Chain Heavy Chain Variable Part Constant Becomes: VL, Vh, CL, Ch1, Ch2, Ch3 CL-Ch1 Connected through disulfide bonds two parts of antibody connected through a Hinge which give the antibody motility divided into Fab (fragment antigen binding) and Fc (Fragment crystalizable region) Antibody Domains: - Variable region - Antigen binding sites - Ch1 region - Determine Allotype - Ch2 region - Binds Complement - Ch3 region - Binds Cells Variants of chains: Light Chain: - Lambda Chain - Kappa Chain Heavy Chain: - Gamma Chain (IgG) - My Chain (IgM) - Alpha Chain (IgA) - Delta Chain (IgD) - Epsilon Chain (IgE) Functions of IgG: - Exists as: Monomeric (plus subtypes) - Amount in Plasma: 75% - IgG is only antibody that pass through placenta. so we get igG from mothers. - Direct Opsonization - Activate Complement System - IgG responsible for the secondary response in humoral immune response because memory B-cells are made to produce IgG Functions of IgM: - Pentameric (with a J-Chain) and Monomeric on B-cells - ''Youngest Class'' since a fetus can produce them. - IgM reacts as the primary response, but no memory as they are produced by T-cell independent B cell proliferation - Complement activation Functions of IgA: - Dimeric (J-chain), Monomeric and Trimeric - Found at mucosal entry - Alpha plasma cells secretes IgA. IgA binds to epithelium through poly IgA receptors and transported through cytoplasm through endocytosis and sent out through proteolytic cleavage - Many microorganisms can cleave IgA Functions of IgD: - Under 1% in blood - Localized on surface of B-cells - Monomeric Functions of IgE: - Very low amount in blood - Monomeric - Mast Cell - Responsible for Type 1 hypersensitivity. Made after sensitization. - Increase amount of IgE during allergic diseases and parasite infections. Differences between Immunoglobulins: - Idiotypic differences: Differ in variable region - Isotypic Differences: Antibodies differ in constant region - Allotypic Differences: Difference between alleles of same constant gene