Скачать с ютуб Microbiology 31| Quantitative Measurement of Bacterial Growth (Part-2) Turbidity & Nitrogen Test в хорошем качестве
bacterial count methods
quantitative methods for bacterial growth
bacterial counting methods
viable count of bacteria
total count of bacteria
quantitative measurement of bacterial growth
methods for bacterial count
direct and viable count of bacteria
bacterial viable and total count methods
microbiology videos
bacterial counting
counting of bacteria
turbidity methods
bacterial counting chamber
counting chamber
bacteria
Quantitative Measurement of Bacterial Growth
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Microbiology 31| Quantitative Measurement of Bacterial Growth (Part-2) Turbidity & Nitrogen Test в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Microbiology 31| Quantitative Measurement of Bacterial Growth (Part-2) Turbidity & Nitrogen Test или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Microbiology 31| Quantitative Measurement of Bacterial Growth (Part-2) Turbidity & Nitrogen Test в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Microbiology 31| Quantitative Measurement of Bacterial Growth (Part-2) Turbidity & Nitrogen Test
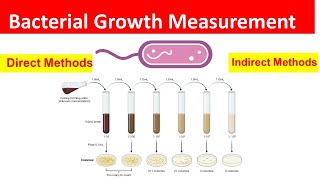
Download "Solution Pharmacy" Mobile App to Get All Uploaded Notes, Model Question Papers, Answer Papers, Online Test and other GPAT Materials - https://play.google.com/store/apps/de... Growth implies that all chemical components of the cell increase with the same speed and after a certain time this leads to an increase in cell number, which causes an increase in size or number of the individuals. Growth is normally performed batch-wise or continuously. Methods for measurement of the cell mass involve both direct and indirect techniques: (1) Direct physical measurement of dry weight, wet weight, or volume of cells after centrifugation. (2) Direct chemical measurement of some chemical component of the cells such as total N, total protein, or total DNA content. (3) Indirect measurement of chemical activity such as rate of O2 production or consumption, CO2 production or consumption, etc. (4) Turbidity measurements employ a variety of instruments to determine the amount of light scattered by a suspension of cells. Using a Haemocytometer = A more accurate method involves using a haemocytometer. This is a specialised microscope slide originally used to count red blood cells. Using the haemocytometer gives total cell counts as it is not possible to distinguish between living and dead cells (you are not required to describe or use a haemocytometer.) Using Turbidimetry= third method, known as turbidimetry, involves using a colourimeter to measure the cloudiness or turbidity of the culture as cell numbers increase. Results are derived by comparison with a standard graph of light absorbance plotted against known cell numbers (You are not required to describe or use a calorimeter). Direct counting methods include microscopic counts using a hemocytometer or a counting chamber. The hemocytometer works by creating a volumetric grid divided into differently sized cubes for accurately counting the number of particles in a cube and calculating the concentration of the entire sample. One can also quantify the number of cells in culture by plating a known volume of the cell culture on a petri dish with a growth medium, which is also known as a streak plate. If the cells are distributed on the plate properly, it can generally be assumed that each cell will give rise to a single colony. Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links- Facebook Group- / solutionpharamcy Facebook Page- / pharmavideo New Channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) / @pharmacydictionary Instagram- / solutionpharmacy E-Mail for official and other work - [email protected] LinkedIn- / pushpendrakpatel #solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #Pharmacognosyvideos #GPATonlinetest #GPATclass #GPATvideos #Microbiologyclass#Microbiology#