Скачать с ютуб Box-Plot (Simply explained and create online) в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Box-Plot (Simply explained and create online) в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Box-Plot (Simply explained and create online) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Box-Plot (Simply explained and create online) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Box-Plot (Simply explained and create online)
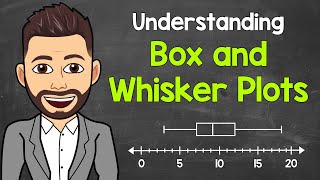
In this tutorial you will learn what a boxplot is, what information can be read in a boxplot and then we will look at what we have learned with an example. Boxplots are used in statistics to graphically display different parameters at a glance. This is why boxplots are so difficult to understand at the beginning, because a lot of information about the data is provided in one diagram. Among other things, the median, the interquartile range and the outliers can be read in a boxplot. The data used must have metric scale level. Such as a person's age, annual household electricity consumption, or temperature. What is the interpretation in a boxplot? The box itself indicates the range in which the middle 50% of all values lie. Thus, the lower end of the box is the 1st quartile and the upper end is the 3rd quartile. Therefore below q1 lie 25% of the data and above q3 lie 25% of the data, in the box itself lie 50% of your data. In the boxplot, the solid line indicates the median and the dashed line indicates the mean. For example, if the median is 34, that means that half of the participants are younger than 34 and the other half are older than 34. The median thus divides the people into two equal groups. The T-shaped whiskers in the boxplot go to the last point, which is still within 1.5 times the interquartile range. What does it mean? The T-shaped whisker is either the maximum value of your data but at most 1.5 times the interquartile range. Therefore, if you have an outlier, then the whisker goes up to 1.5 times the interquartile range. If there is no outlier, the whisker is the maximum value. So the upper whisker is either the maximum value or 1.5 times the interquartile range. Depending on which value is smaller. Exactly the same applies to the lower whisker in the boxplot, which is either the minimum or 1.5 times the interquartile range. Points that are further away are considered outliers. If no point is further away than 1.5 times the interquartile range, the T-shaped whisker thus gives the maximum or minimum value. More information on the boxplot: https://datatab.net/tutorial/box-plot Create boxplot online: https://datatab.net/statistics-calcul...