Скачать с ютуб Neurulation and Organogenesis from Ectoderm / Embryology of Ectoderm в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Neurulation and Organogenesis from Ectoderm / Embryology of Ectoderm в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Neurulation and Organogenesis from Ectoderm / Embryology of Ectoderm или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Neurulation and Organogenesis from Ectoderm / Embryology of Ectoderm в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Neurulation and Organogenesis from Ectoderm / Embryology of Ectoderm
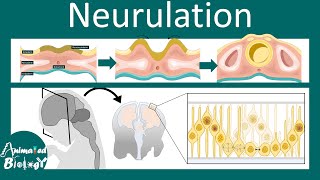
Welcome to my youtube channel power of knowledge academy. In this video you will learn about the process of neurulation, vesiculation and organogenesis from ectoderm in embryonic development. Here is the brief information about the topic that you will see in the video. Gastrulation is a phase that occurs during the third week of early embryonic development, and it takes place immediately after the blastula phase in most animals. Here, the single-layered and hollow blastula is rearranged and differentiated in the multi-layered gastrula with three distinct layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Shortly after the gastrulation phase, the process of neurulation will occur. During this phase, mesodermal cells (middle layer from gastrulation) will form the notochord and will signal overlying ectodermal cells at the neural plate to fold inwardly to form the neural tube, and the joining ends will form the neural crest. The neural tube and neural crest detach from the rest of the overlying ectoderm. The neural tube will become the central nervous system. The neural crest will give rise to the peripheral nervous system, enteric nervous system, melanocytes, facial cartilage, odontoblasts, entero-chromaffin cells, spiral membrane, and more. The ectoderm that fails to involute will form the epidermis of the skin, hair, exocrine glands, and the anterior pituitary. Also, proper development requires communication between the three layers. The neuro-ectoderm will form the neural tube and the neural crest. The neural tube will form the central nervous system (CNS: brain and spinal cord) and control most functions of the body and mind, including control of body movement, thoughts, and homeostasis. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes the nerves and ganglia outside of the CNS and divides into the somatic and autonomic nervous system. The primary function of the PNS is to connect the organs to the CNS, and it forms from the neural crest. The neural crest also gives rise to Schwann cells, chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla, inner ear, cornea, odontoblasts, melanoblasts, pharyngeal arches, and the meninges of the brain and spinal cord. The surface ectoderm will give rise to the epidermis, external glands, hair, nails, anterior pituitary, and the apical ectodermal ridge amongst others. 1. #Ectoderm 2. #Embryology 3. #DevelopmentalBiology 4. #GermLayers 5. #EmbryonicDevelopment 6. #EmbryoFormation 7. #NeuralPlate 8. #EpidermisFormation 9. #EctodermalDerivatives 10. #Neurogenesis 11. #SkinDevelopment 12. #NervousSystemFormation 13. #EmbryonicTissues 14. #CellDifferentiation 15. #Organogenesis