Скачать с ютуб Introduction to Enthalpy | A-level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Introduction to Enthalpy | A-level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Introduction to Enthalpy | A-level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Introduction to Enthalpy | A-level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Introduction to Enthalpy | A-level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel
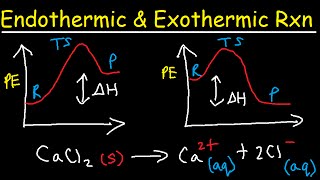
Introduction to Enthalpy in a Snap! Unlock the full A-level Chemistry course at http://bit.ly/2KMCTHM created by Ella Buluwela, Chemistry expert at SnapRevise. SnapRevise is the UK’s leading A-level and GCSE revision & exam preparation resource offering comprehensive video courses created by A* tutors. Our courses are designed around the OCR, AQA, SNAB, Edexcel B, WJEC, CIE and IAL exam boards, concisely covering all the important concepts required by each specification. In addition to all the content videos, our courses include hundreds of exam question videos, where we show you how to tackle questions and walk you through step by step how to score full marks. Sign up today and together, let’s make A-level Chemistry a walk in the park! The key points covered in this video include: 1. Conservation of Energy 2. What is Enthalpy? 3. Standard Conditions 4. System and Surroundings 5. Enthalpy Change 6. Enthalpy Profile Diagrams 7. Activation Energy 8. Enthalpy Terms - Enthalpy Change of: a) Reaction b) Combustion c) Formation d) Neutralisation Conservation of Energy Chemical bonds are the forces of attraction that bind atoms together. Chemical energy lies within these chemical bonds, It is a form of potential energy. In chemical reactions, energy is changed from one form to another. E.g. Chemical Energy may change to thermal energy. No energy is lost. It is converted from one form to another. What is Enthalpy? Enthalpy, H, is the thermal energy that is stored in a system. We can’t measure the directly enthalpy of products and reactants. Instead, we can measure the amount of energy that is absorbed or released to the surroundings. The method in which this is done can vary. You can measure the change in energy by looking at the change in thermal energy. Temperature Increase. Heat gain to surroundings, Heat loss in a chemical system. Temperature Decrease. Heat loss to surroundings, Heat gain in a chemical system. Enthalpy change, ΔH, is the heat energy change at a constant pressure. Standard Conditions Δ - Indicates a change. H - Enthalpy. Θ - Indicates standard conditions. Pressure: 100 KPa (100,000 Pa), Temperature: 298K. Standard states are the states which substances are in under standard conditions. For example, the standard state of water is liquid and the standard state of magnesium is solid. System and Surroundings These are part of the terminology used to discuss components of chemical reactions. System. The chemical reaction. Atoms, Bonds. Surroundings. Everything else! Enthalpy Changes In general, the enthalpy change is the difference between the enthalpy of the products and the reactants. From the overall enthalpy change, we can classify reactions as either: Exothermic: Release Heat. Endothermic: Absorb Heat. Enthalpy Profile Diagrams Exothermic Reactions. The Enthalpy of the products is smaller than the enthalpy of the reactants, The chemical reaction releases heat, There is a heat loss from the system to the surroundings, ΔH is negative. Activation Energy The activation energy is the minimum energy required to start a reaction. It is like rolling a ball to the top of the hill, In order to allow the ball to roll down the other side. Exothermic Reactions. The products have a lower energy than the reactants, Nevertheless, an input of energy is reqyured to break the initial bonds and start the reaction, Once the activation energy has been overcome, the energy output of the reaction provides enough energy to sustain the reaction. The reaction becomes self-sustaining. Endothermic Reactions. The products have a higher energy than the reactants. Enthalpy Change of Reaction The energy change associated with a given reaction. Enthalpy Change of Formation The energy change that takes place when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard state under standard conditions. Enthalpy Change of Combustion The energy change that takes place when 1 mole of a substance is completely combusted. Enthalpy Change of Neutralisation The energy change associated with the formation of 1 mole of water from a neutralisation reaction under standard conditions.