Скачать с ютуб Horizontal Gene Transfer (Transformation, Conjugation, Transduction) в хорошем качестве
conjugation
transformation
horizontal gene transfer
transduction
Horizontal Gene Transfer (Transformation
Conjugation
Transduction)
bacteria
bacterial
gene
transfer
horizontal
protocol
assay
technique
method
animation
animated
explained
explanation
genetics
plasmid
plasmids
process
vector
viral
virus
bacteriophage
system
transfection
konjugation
transduktion
bakterien
types
f plasmid
reproduction
in
bateria
baterial
genetic
laboratrory
competence
competent
cells
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Horizontal Gene Transfer (Transformation, Conjugation, Transduction) в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Horizontal Gene Transfer (Transformation, Conjugation, Transduction) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Horizontal Gene Transfer (Transformation, Conjugation, Transduction) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Horizontal Gene Transfer (Transformation, Conjugation, Transduction)
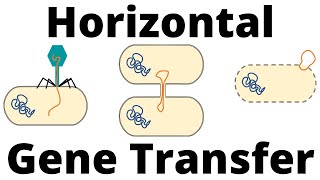
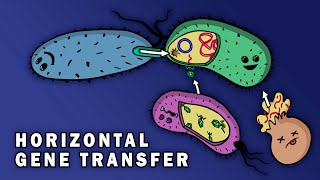
Gene transfer refers to how DNA gets passed between organisms. When genes get passed from parent to offspring, we call this vertical gene transfer (because it goes down the generations). Now, when genes are transferred between two already existing organisms, we call this horizontal gene transfer. This type of gene transfer is often beneficial for the recipient as it allows the bacteria to produce new proteins, granting new functionality. This can even give selective advantage in the form of for example antibiotic resistance. The 3 main types of horizontal gene transfer include transformation, conjugation and transduction. Transformation is when a bacteria takes in free genetic material from the environment, usually in the form of a free floating plasmid and can either be integrated into the bacterial chromosome or exist as a plasmid. How well bacteria can take in foreign DNA in this manner is known as their competence. Conjugation is when genetic material is transferred between two bacteria by direct contact and is carried out in 4 main steps: 1. Donor bacteria produces a pilus 2. Donor uses the pilus to attach and draw the recipient and itself closer to each other 3. The mobile plasmid in the donor is nicked, thereby turning the double stranded plasmid into two single stranded plasmids and one of these is transferred to the recipient cell 4. Finally, both cells synthesize a complementary strand to produce a double stranded circular plasmid and they also reproduce pili, meaning that both cells are now viable donors In transduction a viral agent is used to transfer DNA between two bacteria. In nature this may occur when a virus infects a bacterial cell and the viral DNA is integrated in the bacterial genome. When new viruses are created inside of the bacteria, some of the bacterial DNA may accidently be incorporated into the viral DNA and in this way transferred to the next bacteria, these new viruses infect. Viral vectors can be used in the lab to integrate genes of interest into the genome of eukaryotic cells.